How to set up zone flags
Resources
Example application: A demo application is available on GitHub.
Concepts
The patching mechanism
API patching or monkey-patching means we take an existing API and override its behavior globally or in specific places.
An example on what zone.js is doing under the hood can look like this:
const originalMethod = EventTarget.prototype.addEventListener;
const patchedAddEventListener = (eventName, originalCallback, useCapture) => {
console.log(`Add event listener for ${eventName}`);
const patchedCallback = (event) => {
console.log(`Fire ${eventName} callback for with event ${event}`);
if (__zone_symbol__UNPATCHED_EVENTS.includes(eventName)) {
return originalCallback(event);
}
// wrap callback in zone
};
return originalMethod.apply(this, [type, patchedCallback, useCapture]);
};
EventTarget.prototype.addEventListener = patchedAddEventListener;
Here we patch the global addEventListener API.
Every fired event in the Browser will now pass our patch from above.
The flagging mechanism
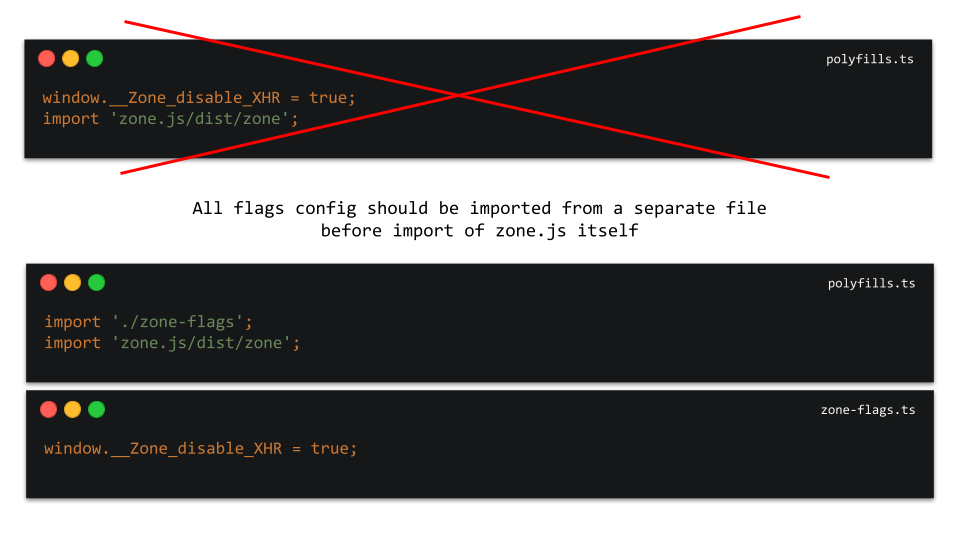
When zone.js is first time initialized on the page, it takes values of flags already located in window object.
So it's important to set them before zone.js is init. So we need to inject zone-flags.js code above the zone code.
import './zone-flags';
import 'zone.js/dist/zone';
It is not efficient to do like that:
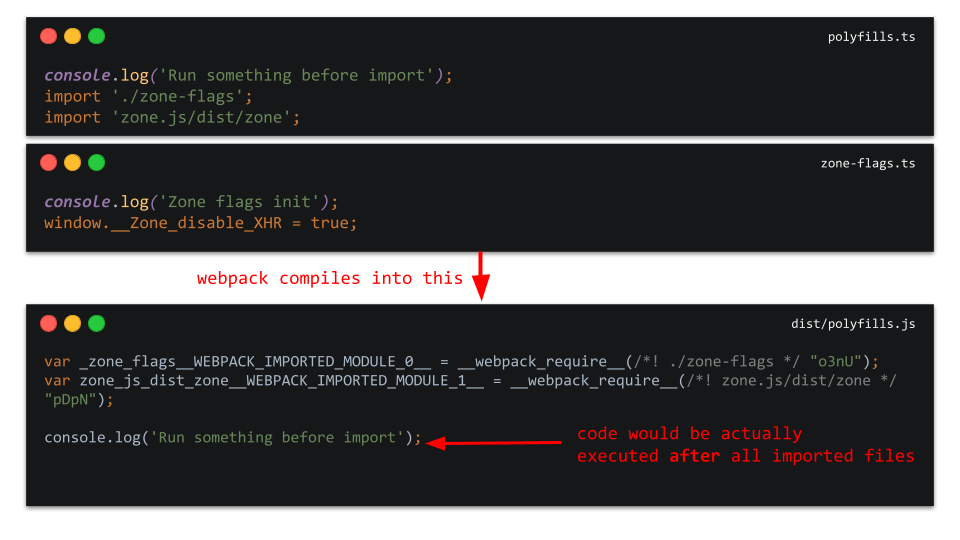
window.__Zone_disable_XHR = true;
import 'zone.js/dist/zone';
Because all imports get hoisted by webpack and then imported code is injected into a bundle before any meaningful JS in the file itself.
Set up using vanilla JavaScript
- Create file
zone-flags.tsparallel to yourpolyfills.tsand insert the following content:
(window as any).__Zone_disable_requestAnimationFrame = true;
(window as any).__Zone_disable_timers = true;
(window as any).__zone_symbol__UNPATCHED_EVENTS = [
'load',
'error',
'close',
'open',
];
(window as any).__Zone_disable_XHR = true;
- In
polyfills.tsabove the zone import, importzone-flags.ts:
// ☝️ Make sure zone-flags are imported before zone.js
import './zone-flags';
// Zone JS is required by default for Angular itself.
import 'zone.js/dist/zone';
Set up using @rx-angular/cdk/zone-configuration helpers
- Create file
zone-flags.tsnext to yourpolyfills.tsand insert the following content:
import { zoneConfig } from '@rx-angular/cdk/zone-configurations';
zoneConfig.global.disable.requestAnimationFrame();
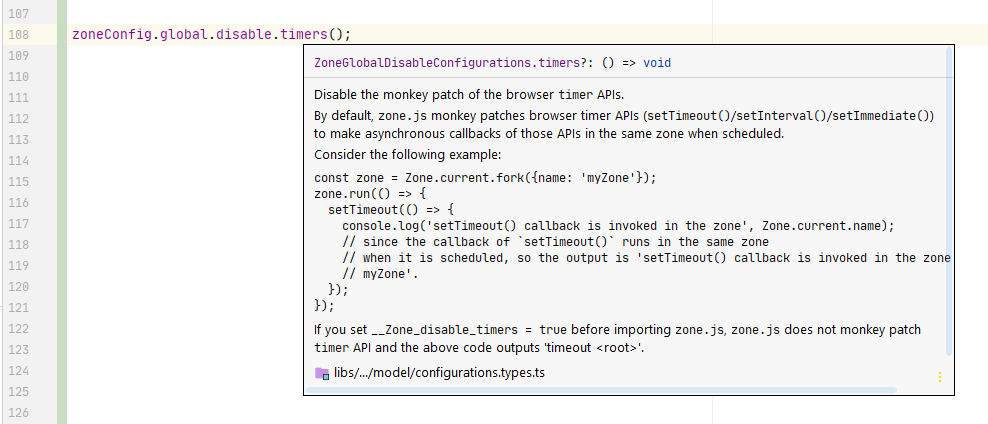
zoneConfig.global.disable.timers();
zoneConfig.events.disableXHR();
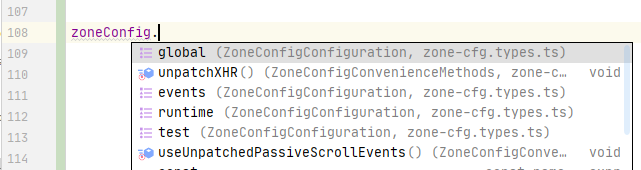
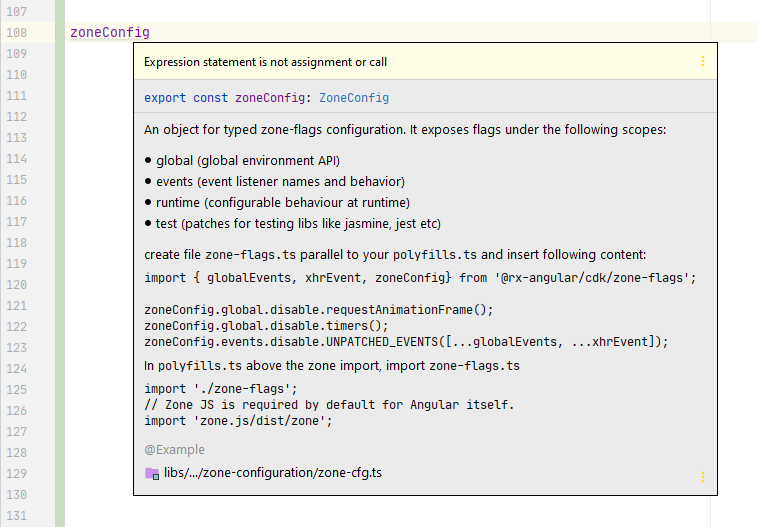
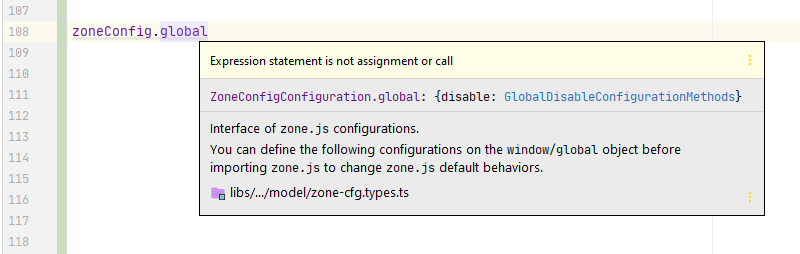
In this file, we disable some global APIs and a couple of DOM events by using the typed methods and extra convenience methods.
As you type, you will see zoneConfig provides autocompletion:
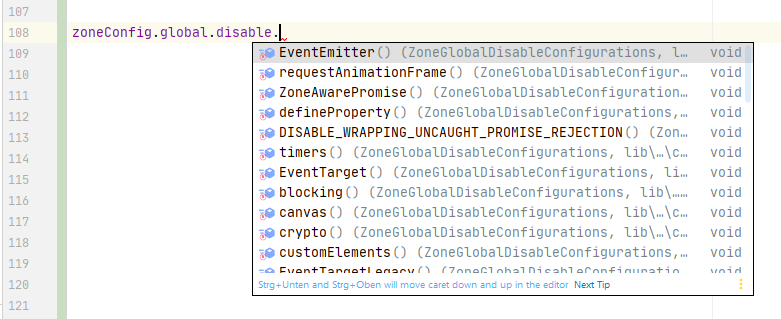
As well as inline documentation of scopes, methods and configuration details in the IDE:
- In
polyfills.tsabove the zone import, importzone-flags.ts:
// ☝️ Make sure zone flags are imported before zone.js
import './zone-flags';
// Zone JS is required by default for Angular itself.
import 'zone.js/dist/zone';
💡 Pro Tip: >
@rx-angular/cdk/zone-configurationerrors if it is used incorrectly. If you used zone-flags wrong (not executing it before zone.js runs) you should see the following error in the console:
Configure Zone runtime settings using @rx-angular/cdk/zone-configuration helpers
- Create file
zone-runtime.tsparallel to yourpolyfills.tsand insert the following content:
import { zoneConfig } from '@rx-angular/cdk/zone-configurations';
zoneConfig.runtime.disable.ignoreConsoleErrorUncaughtError();
- In
polyfills.tsbelow the zone import, importzone-runtime.ts:
// Zone JS is required by default for Angular itself.
import 'zone.js/dist/zone';
// ☝️ Make sure zone flags are imported before zone.js
import './zone-runtime';
💡 Pro Tip: >
@rx-angular/cdk/zone-configurationerrors if it is used incorrectly. If you used zone-runtime configurations wrong (not executing it after zone.js runs) you should see the following error in the console:

